Load file specifications
Using Epiq Discovery, you can load natives, image files, and extracted text provided from third-party applications. When loading and importing data, make sure that the Load folder contains the appropriate files and folders, and that the DAT, OPT, and LST file contents appear in the proper format. This topic explains the required folders, files, and file structure (for example fields, paths, and delimiters).
Make sure to keep the load folder and files intact, exactly as the third-party tool created them. After verifying that the data you want to import meets these requirements, refer to the Load production topic for instructions on how to perform the Load.
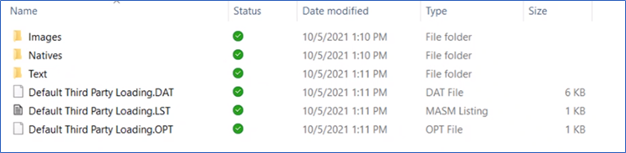
Load folder
The Load folder contains everything you need to load. The following figure shows the structure required to properly load data. The path to the Load folder is the relative path. The relative path requires folders for the Images, Natives, and Text files as shown. In addition, the DAT, OPT, and LST files appear on the same level as these folders.
OPT file
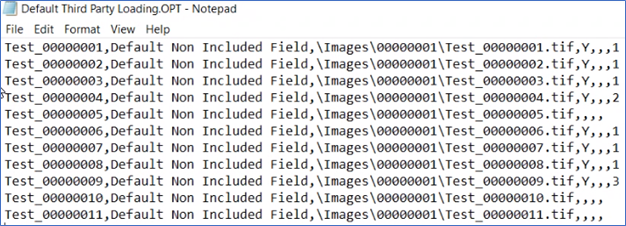
The Image Load file, a Concordance OPT file, lists each image per line in the standard format, beginning with the number, relative path, and so on.
-
Document Number. The identifier for Document Number must match in the OPT and DAT files. For example, if the DAT file uses BatesNumber, the OPT must use BatesNumber.
-
Path to the file. Epiq Discovery uses relative paths from the Load folder to find the images. The file path must contain the correct path to the image file from the Load folder so that Epiq Discovery can locate the image file.
-
Commas. Verify that each line in your OPT file uses six commas to delineate the seven standard fields, as shown in the following example. Comma delineators must be used. If your OPT file contains another type of delineator, update your OPT file to use commas.
The following figure shows an example OPT file.
The following table shows the required fields in the OPT file in order. Each line in the OPT file requires a specific number of comma delimiters, even if the fields are not used.
| Field | Description |
| 1 | Identifies the document that contains the image page, which must match a number in the DAT file. |
| 2 |
Volume identifier, this field is optional when the DAT and OPT files are encoded as follows:
If the DAT and OPT files use different character encoding, then this field is required (see "Default Non Included Field" in the figure above). |
| 3 | Path to the image to be loaded. The path must be either the relative path from the location of the OPT file or the fully qualified path. |
| 4 | Indicates if the image is the first page of the document with a “Y”. Entries with a “Y” match the document's BEGDOC. |
| 5 | Folder, which is not used. |
| 6 | Box, which is not used. |
| 7 | Optional page count. |
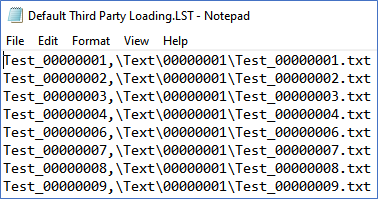
LST file
The Text Load file (LST) file lists each extracted text file on a single line by number and relative file location. Verify that your LST uses commas to delineate the fields, as shown in the following example.
The fields expected in the LST file appear below, separated by a comma delimiter.
| Field | Description |
| 1 | Identifies the document associated with the text, which must match a number in the DAT file. |
| 2 | Path to the text file. The path must be either the relative path from the location of the LST file or the fully qualified path. |
DAT file
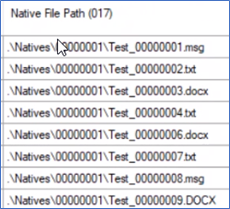
The DAT file is standard eDiscovery format when viewed using a DAT file reader application. The first row of the DAT file contains the column names in the file. When loading the DAT file, you identify the delimiter used in the file.
Verify that your Native File Path and any other file paths, like Text File Path begins with a period (.), as shown in the following example. The period denotes the relative path to the file, starting from the Load folder.
Epiq Discovery supports the following file encoding, which you select during the load: Unicode, Unicode (Big Endian), Unicode (UTF- 8) or Western European (Windows) encoding.
Supported date formats for import
When loading jobs though Desktop Client, the system supports common date fields with year designations. Supported date formats appear in the following tables.
Supported Date Formats
| Description | Delimiter: / | Delimiter: - | Delimiter: . | Delimiter: none |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Begin with month | MM/dd/yyyy | MM-dd-yyyy | MM.dd.yyyy | MMddyyyy |
| Begin with year | yyyy/MM/dd | yyyy-MM-dd | yyyy.MM.dd | yyyyMMdd |
Supported Date and Time Formats
In addition to the time formats mentioned in the below table, loading also reads hours in single-digit 12-hour format (h:mm aa).
| 12-hour format | 24-hour format | 12-hour with seconds | 24 hour with seconds |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM/dd/yyyy hh:mm aa | MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm | MM/dd/yyyy hh:mm:ss aa | MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss |
| MM-dd-yyyy hh:mm aa | MM-dd-yyyy HH:mm | MM-dd-yyyy hh:mm:ss aa | MM-dd-yyyy HH:mm:ss |
| MM.dd.yyyy hh:mm aa | MM.dd.yyyy HH:mm | MM.dd.yyyy hh:mm:ss aa | MM.dd.yyyy HH:mm:ss |
| yyyy/MM/dd hh:mm aa | yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm | yyyy/MM/dd hh:mm:ss aa | yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss |
| yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm aa | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm | yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss aa | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss |
| yyyy.MM.dd hh:mm aa | yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm | yyyy.MM.dd hh:mm:ss aa | yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss |
|
dd/MM/yyyy hh:mm aa |
dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm |
dd/MM/yyyy hh:mm:ss aa |
dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss |
|
MM/dd/yy hh:mm aa |
MM/dd/yy HH:mm |
MM/dd/yy hh:mm:ss aa |
MM/dd/yy HH:mm:ss |
|
MM-dd-yy hh:mm aa |
MM-dd-yy HH:mm |
MM-dd-yy hh:mm:ss aa |
MM-dd-yy HH:mm:ss |
|
MM.dd.yy hh:mm aa |
MM.dd.yy HH:mm |
MM.dd.yy hh:mm:ss aa |
MM.dd.yy HH:mm:ss |
|
yy/MM/dd hh:mm aa |
yy/MM/dd HH:mm |
yy/MM/dd hh:mm:ss aa |
yy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss |
|
yy-MM-dd hh:mm aa |
yy-MM-dd HH:mm |
yy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss aa |
yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss |
|
yy.MM.dd hh:mm aa |
yy.MM.dd HH:mm |
yy.MM.dd hh:mm:ss aa |
yy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss |
|
dd/MM/yy hh:mm aa |
dd/MM/yy HH:mm |
dd/MM/yy hh:mm:ss aa |
dd/MM/yy HH:mm:ss |
|
m/d/yy hh:mm aa |
m/d/yy HH:mm |
m/d/yy hh:mm:ss aa |
m/d/yy HH:mm:ss |
|
m-d-yy hh:mm aa |
m-d-yy HH:mm |
m-d-yy hh:mm:ss aa |
m-d-yy HH:mm:ss |
| yyyy dd MMM hh:mm aa | yyyy dd MMM HH:mm | yyyy dd MMM hh:mm:ss aa | yyyy dd MMM HH:mm:ss |
| MMM dd yyyy HH:mm aa | MMM dd yyyy HH:mm | MMM dd yyyy hh:mm:ss aa | MMM dd yyy HH:mm:ss |
| dd MMM yyyy hh:mm aa | dd MMM yyyy HH:mm | dd MMM yyyy hh:mm:ss aa | dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss |
| yyyyMMDDhhmmssaa | yyyyMMddHHmmss |